Taming extreme aerodynamic flows with generalized super resolution and manifold identification
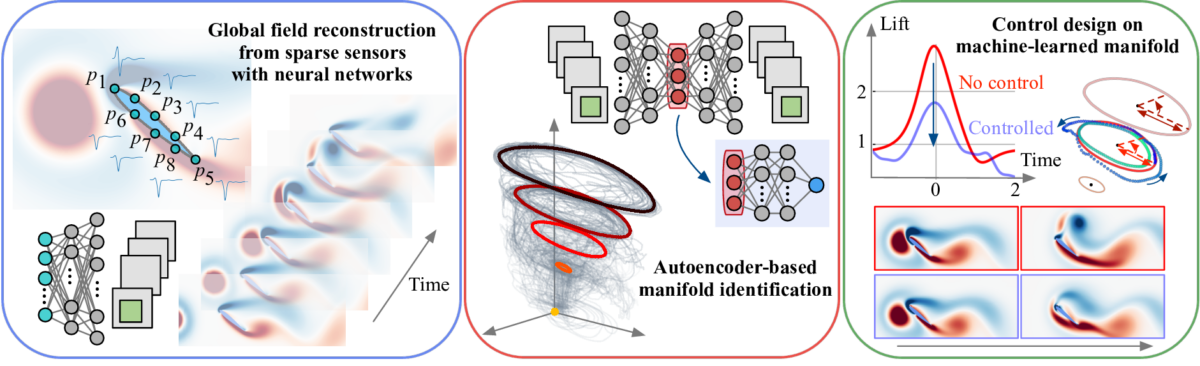
Modern small aircraft are asked to operate under severe atmospheric conditions in urban areas and turbulent wakes behind large structures. Complex aerodynamics in such extreme air space are generally determined by interactions between a strong gust and a wing. However, there is a huge parameter space of extremely strong gust-wing interactions, making a naive parameter sweep with expensive simulations and experiments impractical. In this talk, we discuss how such extremely complex aerodynamics can be analyzed in a data-driven manner from the aspect of global field reconstruction, reduced-complexity modeling, and flow control. We first consider global field reconstruction from sparse sensors through the lens of generalized super-resolution analysis. This talk covers not only fundamental applications of fluid-flow super resolution but also practical uses for moving sensor conditions and industrial turbulence. To perform flow control leveraging the reconstructed fields from sparse sensors, we then aim to construct a control strategy of flows in a low-order subspace identified by nonlinear machine-learning-based data compression. Although it is challenging to analyze the nonlinear, transient nature of extreme aerodynamics with conventional linear techniques, we reveal that the underlying physics of a collection of time-varying vortical flows in a high-dimensional space can be expressed on a low-rank manifold leveraging the present data-driven compression. It is also demonstrated that efficient control strategies can be derived at a minimal cost with the assistance of phase-amplitude reduction on the discovered manifold. These developed data-driven strategies provide a new perspective on reconstructing, modeling, and controlling a range of extremely unsteady flows.